Nuxt SWR
This mode employs a technique called stale-while-revalidate, which enables the server to provide stale data while simultaneously revalidating it in the background. The server generates an HTML response on demand, which is then cached. When deployed, the caching specifics can vary depending on the provider (eg. Vercel, Netlify, etc.), and information about where the cache is stored is usually not disclosed. There are two primary settings for caching:
- No TTL (Time To Live): This means the response is cached until there is a change in the content. To enable this mode, set up a route rule in
nuxt.configas follows:
export default defineNuxtConfig({
routeRules: {
"/swr_no_ttl": { swr: true },
},
})- TTL Set: This implies that the response is cached until the set TTL expires. To enable this mode, set up a route rule in nuxt.config as following:
export default defineNuxtConfig({
routeRules: {
"/swr_ttl": { swr: 60 },
},
})Nuxt saves the API response that was used for generating the first version of the page. Then upon all subsequent requests, only the API gets called, until the response changes. When a change is detected during a request – with no TTL set – or when the TTL expires, the server returns the stale response and generates new HTML in the background, which will be served for the next request.
SWR (Stale-While-Revalidate) 是 HTTP 快取的策略,這種策略的核心就是能夠允許客戶端可以先使用快取的資料,並同時在背景中驗證快取資料是否已經過期,如果過期表示需要進行更新,就會重新的抓取資料並更新至快取中 (畫面上不會重新渲染成新的資料),而當再次有請求時,就會拿到剛剛已經更新過的快取資料。
而 SWR (Stale-While-Revalidate) 的快取策略,在伺服器端請求回應的回應標頭 (Response header) 中包含一個名為 Cache-Control 的選項,用來控制頁面的快取策略。
在 Nuxt 3 中你也可以在路由策略中,使用 SWR 來實現快取的策略,你可以透過添加 swr 選項來做控制。
export default defineNuxtConfig({
routeRules: {
'/articles/*': { swr: 3600 }
}
})以上面的設定來說,文章相關的頁面 /articles/** 會設定 SWR 快取策略,傳入數值則表示過期的時間 3600 秒。
當我們瀏覽文章頁面時,可以發現瀏覽器收到的請求回應(例如回應文字 Nuxt v1),回應標頭的 Cache-Control 如下設定:
s-maxage=3600, stale-while-revalidates-maxage 選項,作為回應的新鮮時間,也就是多久後才視為過期的舊資料,3600 則表示一小時內再次發送的請求將會從快取中取得資料。
s-maxage 和 max-age 其實稍微有點不大一樣,max-age 可以用來指定任何的快取的快取時間,而 s-maxage 同樣是設定快取的時間,但是只適用於共享快取,例如代理伺服器 Proxy、網站透過 Nginx 進行反向代理伺服器或 CDN 的共享快取。
Cache-Control 的 stale-while-revalidate 選項,可以傳入一個時間秒數,來驗證頁面快取的時間是否已經超過所設定的秒數,如果超過則會向伺服器發送請求來取得資料,剛好回應的資料文字變更為 Nuxt v2,就會寫入到快取中提供給未來的請求做使用。
所以當我們再次重新整理頁面,如果快取中存在頁面資料,則會依然從快取中做回應,而這一次所拿到的資料就是剛剛重新取得的新資料 Nuxt v2。
{ swr: 3600 } 設定所產生的 Cache-Control: s-maxage=3600, stale-while-revalidate,表示頁面的快取時間為一小時,而因為 stale-while-revalidate 沒有傳入時間,表示除了直接回應快取中的資料 Nuxt v1 文字外,它也會同時在背景重新驗證快取的資料是否過期,如果過期就會發送請求至伺服器端請求資料,並再資料真的有變動時,更新新的資料到快取之中,不過呢,畫面上是不會重新顯示新資料的,仍維持 Nuxt v1 文字,使用者下次重新進入頁面才會再從快取中取得新資料 Nuxt v2。
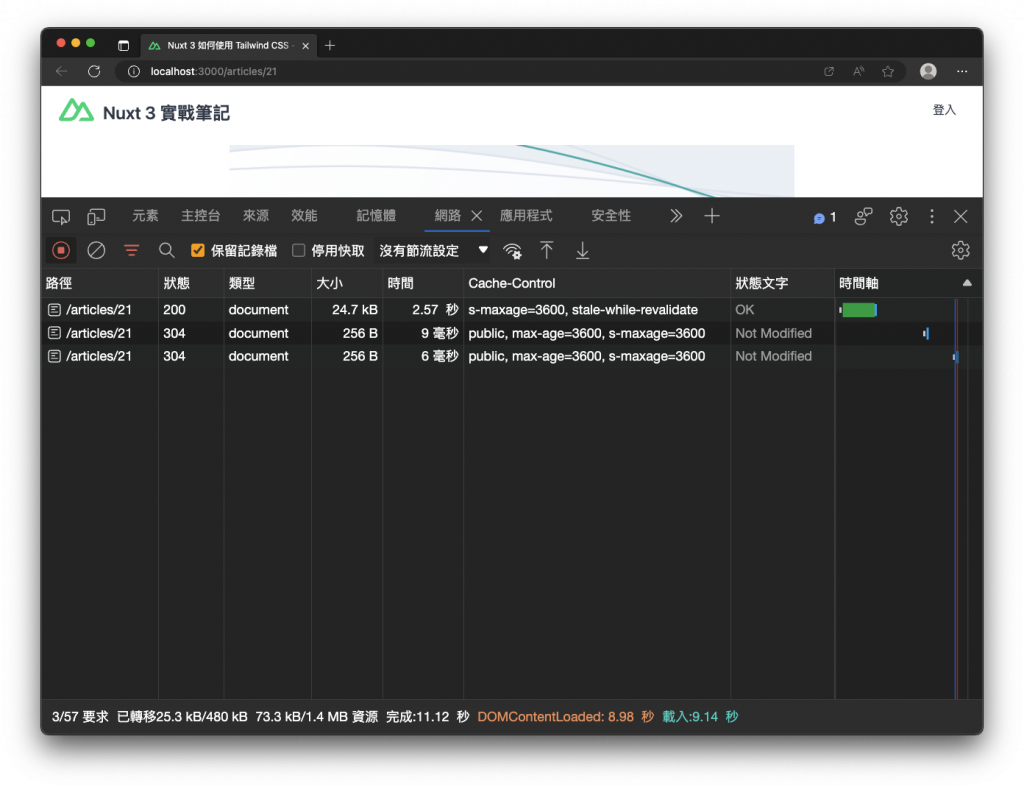
透過這樣子的方式,只有在首次沒有快取的情況下會最花費時間,使用者最明顯感覺到畫面的載入,爾後快取的驗證與重新取的資料,都是在背景做執行,使用者再次重新瀏覽網頁,就會從快取中取得資料,這樣一來畫面的載入就會非常的快速。
總結來說,SWR (Stale-While-Revalidate) 的核心概念,就是嘗試拿快取中的資料作為回應,並同時在背景中,驗證快取是否過期來重新取得最新的資料來,並將新資料更新到快取中提供給未來的請求做使用,因此使用者在瀏覽網頁時便不在需要等待伺服器端渲染 HTML 與回傳的時間。
實際上 Cache-Control 可以控制的快取策略也有許多不同的選項,如果 Nuxt 3 預設的 SWR 還不夠滿足你,那麼就需要自己來做定義回傳,更多的選項功能可以參考 Cache-Control - HTTP | MDN。
Reference
Comparing Nuxt 3 Rendering Modes: SWR, ISR, SSR, SSG, SPA - RisingStack Engineering