Quick Sort
In merge sort, the divide step does hardly anything, and all the real work happens in the combine step. Quicksort is the opposite: all the real work happens in the divide step. The mechanism works like this:
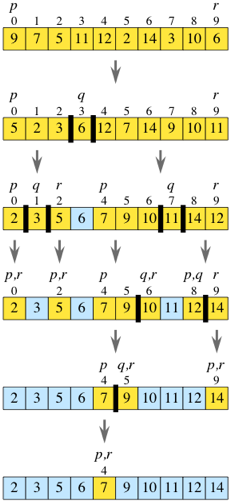
Choose the right-most element (actually any element will do) as the pivot, then rearrange the elements so that all elements smaller than the pivot is on the left side, while elements larger than the pivot is on the right side. Recursively do this process until no element is in the sub-array.
Partition step
Another explanation of the partition step
The rearrange step is called partition, and is actually the hardest part. the idea is:
-
Iterate the array, if the item
arr[j]is less than the pivot, we put it ingroup L(less group). if the itemarr[j]is greater than the pivot, we put in ingroup G(greater group). continue the process until the iteration ends, it sounds easy, but how to actually put the item in the correct group? we will use a swap strategy. -
Apart from cursor
j(the iteration cursor, always advances by 1 in each iteration), we also need to have cursorq, its purpose is to separategroup Landgroup G, it might or might not advance in each iteration. -
When
arr[j]is less than the pivot, we swap it with the left-most item ingroup G, and advancesqby 1. <--- this is the most important step, the idea is to put the item in correct group as well as to expand the boundary ofgroup L. -
When
arr[j]is greater than the pivot, nothing needs to be done, because it already is in the correct group. -
When finish iteration, position
qis the position we should insert the pivot, because it is the separation line betweengroup Landgroup G.
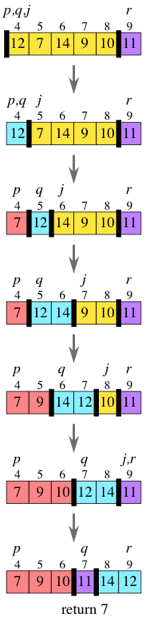
Implementation
var swap = function (array, firstIndex, secondIndex) {
var temp = array[firstIndex];
array[firstIndex] = array[secondIndex];
array[secondIndex] = temp;
};
var partition = function (array, p, r) {
var q = p;
for (var i = p; i < r; i++) {
if (array[i] <= array[r]) {
swap(array, i, q);
q++;
}
}
swap(array, r, q);
return q;
};
var quickSort = function (array, p, r) {
if (p < r) {
var q = partition(array, p, r);
quickSort(array, p, q - 1);
quickSort(array, q + 1, r);
}
};def partition(array, low, high):
# choose the rightmost element as pivot
pivot = array[high]
# pointer for greater element
i = low - 1
# traverse through all elements
# compare each element with pivot
for j in range(low, high):
if array[j] <= pivot:
# if element smaller than pivot is found
# swap it with the greater element pointed by i
i = i + 1
# swapping element at i with element at j
(array[i], array[j]) = (array[j], array[i])
# swap the pivot element with the greater element specified by i
(array[i + 1], array[high]) = (array[high], array[i + 1])
# return the position from where partition is done
return i + 1
def quickSort(array, low, high):
if low < high:
# find pivot element such that
# element smaller than pivot are on the left
# element greater than pivot are on the right
pi = partition(array, low, high)
# recursive call on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1)
# recursive call on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high)
data = [8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6]
quickSort(data, 0, len(data) - 1)
print(data)
Complexity
Stability: No
Space complexity: O(log n)
Time Complexities
-
Worst Case Complexity:
O(n^2)It occurs when the pivot element picked is either the greatest or the smallest element. This condition leads to the case in which the pivot element lies in an extreme end of the sorted array. One sub-array is always empty and another sub-array contains n - 1 elements. Thus, quicksort is called only on this sub-array. However, the quicksort algorithm has better performance for scattered pivots. -
Best Case Complexity:
O(n*log n)It occurs when the pivot element is always the middle element or near to the middle element. -
Average Case Complexity:
O(n*log n)It occurs when the above conditions do not occur.